Which Statement is NOT part of the cell theory. Viruses Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes are made of cells.

Bacteria Cell Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
A typical bacterial cell have.

. Actively block water molecules from entering the cell d. Bacterial cell walls are made of a substance called peptidoglycan D. 39 A bacterial cell MUST CONTAIN all of the following structures EXCEPT for a.
Flagella which are long flexible structures made from the protein flagellin extend out from the cell wall and give the bacterial cell added motility. This problem has been solved. The abbreviation for the genetic material of all cells is ___.
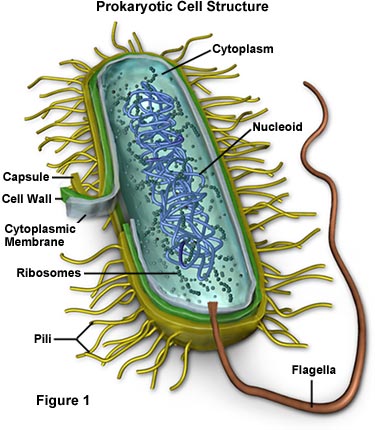
The bacterial nucleus is known as nucleoid. Bacterial cells prokaryotic cells are structurally much simpler than eukaryotic cells and the two cell types are compared in Table 32. Move materials and organelles in the cell.
A bacterium contains the following cell structures does not contain a nucleus from BIOL 1103 at University Of Georgia. Contain a cell wall composed of peptidoglycan. Calls that have DNA located in a nucleoid region of the cytoplasm are called _______ cells.
Some of the structures inside a cell that help it live to perform its role in an organism are chloroplasts mitochondria ribosomes and the nucleus. See the answer See the answer done loading. It is commonly hijacked by invading pathogens and is also responsible for transport networks in the cell.
The reason that bacterial cells are more resistant to osmotic shock than are eukaryotic cells is that they. The bacterial cell is protected and contained by a cell wall which is made from peptidoglycan a sugar and protein polymer. In most bacteria the most numerous intracellular structure is the ribosome the site of protein synthesis in all living organisms.
Group of answer choices Choose that apply. It lacks all membrane bound cell organelles such as mitochondria lysosome golgi endoplasmic reticulum chloroplast peroxisome glyoxysome and true vacuole. Composed of lipopolysaccharides phosholipids porins and chains of alternating n-acetylglucosamine and n-acetylmuramic acid that are covalently bound together.
Some bacteria have a capsule surrounding the cell made of a sticky polysaccharide or protein. Bacteria also lacks true membrane bound nucleus and nucleolus. Contain actin and work with motor proteins.
The cell wall is the outermost component common to all bacteria except Mycoplasma species which are bounded by a cell membrane not a cell wall. Are selectively permeable e. The cytoplasm plasma membrane nucleoid and ribosomes are found in all bacterial cells.
Some bacteria stain gram-positive and others stain gram-negative because of differences in the structure of their. Contain a cell wall composed of cellulose b. The 70S ribosome is made up of a 50S and 30S subunits.
Some bacteria have surface features external to the cell wall such as a capsule flagella and pili which are less common components and are discussed next. A Ribosomes B Nucleoid C Plasma Membrane D Cell Wall. Bacterial cells have all of the following structures EXCEPT a cell wall.
32 A Typical Bacterial Cell 1. Periplasmic flagella axial filaments. Bacterial flagella rotate to propel the cell E.
_ What do bacterial cells contain. Structure of Bacterial Cell. The framework of the prokaryotic cell wall is.
Which of the following bacterial structures is never involved in attachment to host cells. A a nucleus B mitochondria C four chromosomes D DNA Get the answers you need now. Alternating hydrophobic and hydrophilic layers of phospholipid with peripheral and integrally bound proteins.
Protection found in some microbial eukaryotes which enables a surface that can engulf prey. The cell walls of gram-positive bacteria contain. A Lipoprotein B Peptidoglycan C Phospholipid D Chitin.
All prokaryotes have 70S where S Svedberg units ribosomes while eukaryotes contain larger 80S ribosomes in their cytosol. Have 70S ribosomes as the major ribosome type no 80S ribosomes. Bacteria have a single circular chromosome made of double-stranded DNA C.
Discuss the factors that determine the size and shape of a bacterial cell. Bacteria with thick cell walls are referred to as gram-positive while those with thin cell walls surrounded by a lipid membrane are called gram-negative. Found in cilia and flagella.
Distinguish a typical bacterial cell from a typical plant or animal cell in terms of cell shapes and arrangements size and cell structures 2. Bacteria can have membrane-enclosed organelles such as mitochondria or chloroplasts B. They consists of various cell surface structures cell wall plasma membrane many cytoplasmic inclusions and the bacterial chromosome nucleoid.
Bacterial cell have simpler internal structure. Contain Osmo- regulating porins c. 40 Gram positive bacteria can be distinguished from gram negative bacteria by the staining of a thick cell wall composed of the macromolecule.
Used for cell motility division and muscle contraction. Capsules fimbriae pili flagella and even the cell wall are not found in all bacteria. Surface components capsule cell wall fimbriae flagella are.
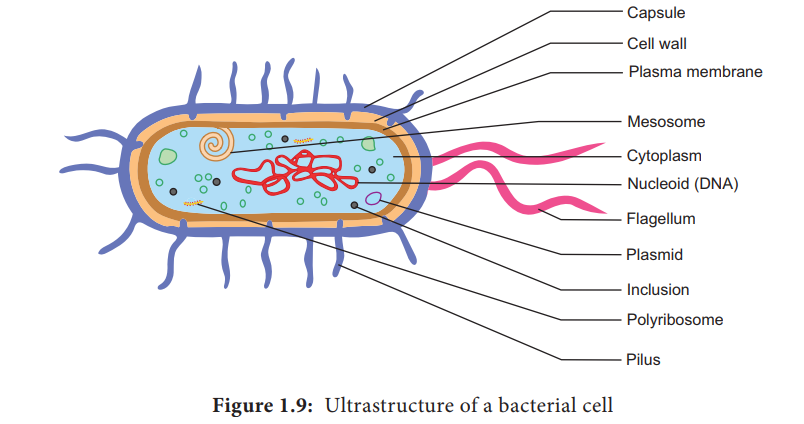
Ultrastructure Of A Bacterial Cell With Diagram
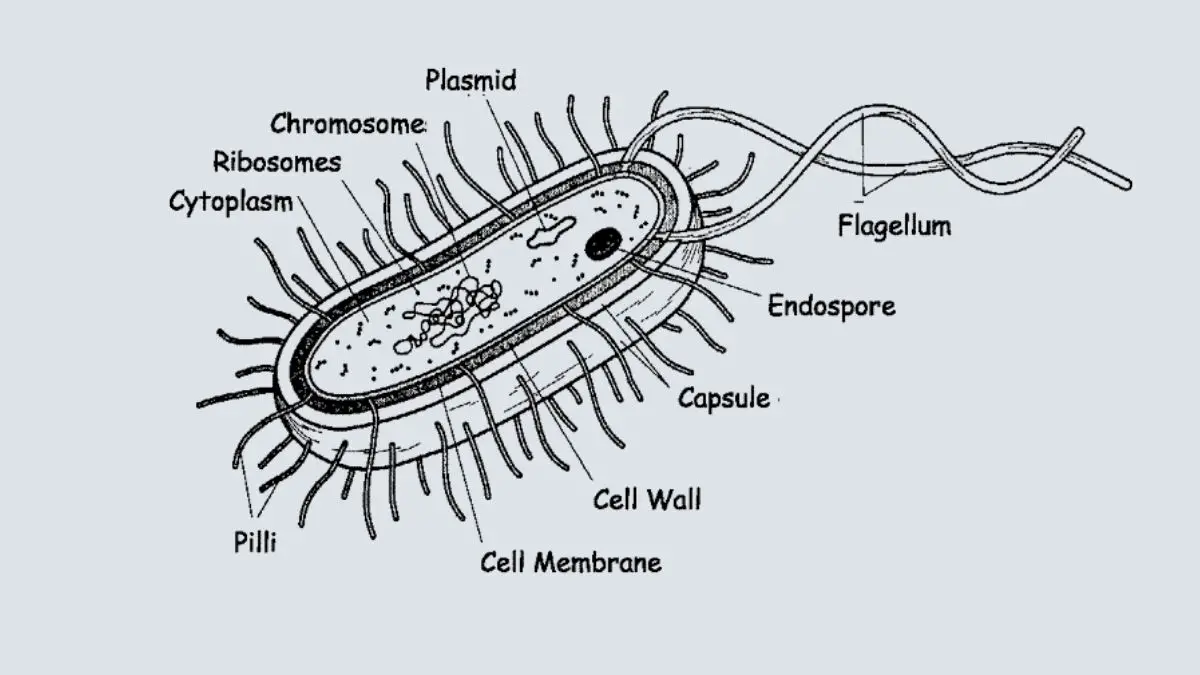
What Is Bacteria Types Structure Shapes Morphology Nutrition Growth Habitat Reproduction Examples

Prokaryotic Cell Definition Examples Structure Biology Dictionary
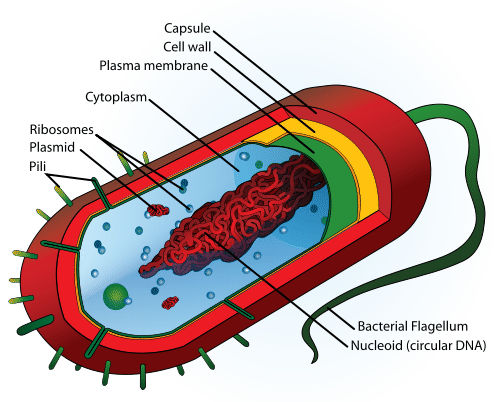
Bacteria Characteristics Read Biology Ck 12 Foundation

Bacteria Cell Evolution Classification Britannica
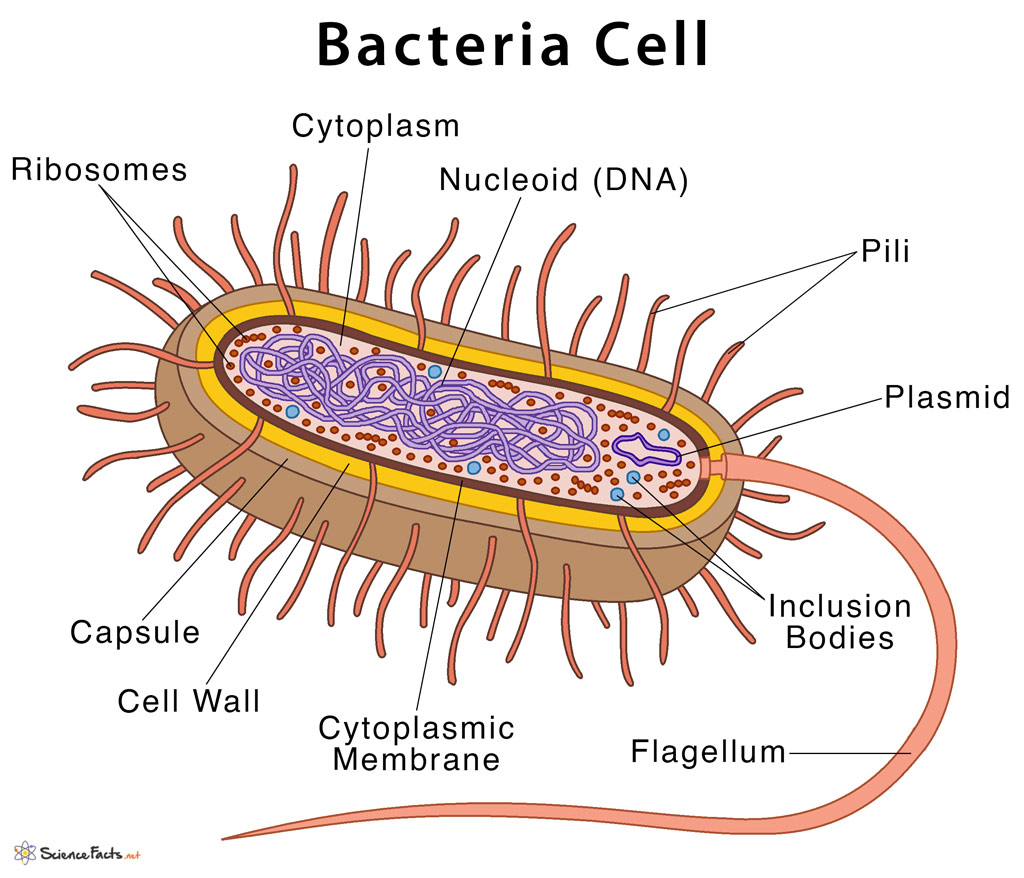
Bacteria Definition Characteristics With Examples Diagram

Components Of Bacterial Cell 7 Components With Diagram
Prokaryotes Vs Eukaryotes Similarities Differences Identification

0 Comments